What is a Temperature Data Logger? How it works?
- Mettcover Global
- February 27, 2023
Temperature Data Loggers:
Temperature data loggers are electronic devices that measure and record temperatures over time. These devices typically consist of a temperature sensor, a data storage unit, and a battery or power source. Some data loggers also feature communication interfaces, such as USB or Ethernet ports, which allow the data to be easily transferred to a computer or other smart devices.
One of the best use cases of temperature data loggers in the cold chain is in the pharmaceutical industry; to monitor the temperature of drugs and vaccines while in transit. Pharmaceutical products are often temperature-sensitive and can be damaged or rendered ineffective if they are exposed to temperatures outside of the specified range. Using temperature data loggers, pharmaceutical companies can monitor the temperature of their products throughout the supply chain to ensure that they are stored and transported at the appropriate temperature. This helps to maintain the potency and efficacy of the drugs and vaccines, and to prevent waste.

Temperature data loggers are also used in the food industry or in the perishables cold-chain. By using temperature data loggers, food companies can monitor the temperature of their products throughout the entire supply chain, from farm to fork. This helps to ensure that food is stored at the appropriate temperature to prevent spoilage and foodborne illness.
Temperature Recorders for Shipping Food and Perishables
Temperature Data Loggers are widely used in the cold chain to monitor temperature integrity and profiles while transporting, stocking and storing temperature-sensitive perishables, such as Agricultural Produce, Wine, Dairy Products and Chocolate. By using temperature data loggers, companies can monitor the temperature of their products in storage and take corrective action in case of any undesirable temperature excursion. For example, if the temperature of a storage facility exceeds the specified range, temperature data loggers will record the event and companies can take immediate corrective action to adjust the temperature control system or to move the products to a different location. Some data loggers also come with in-built alarm features to highlight any breach in real time.

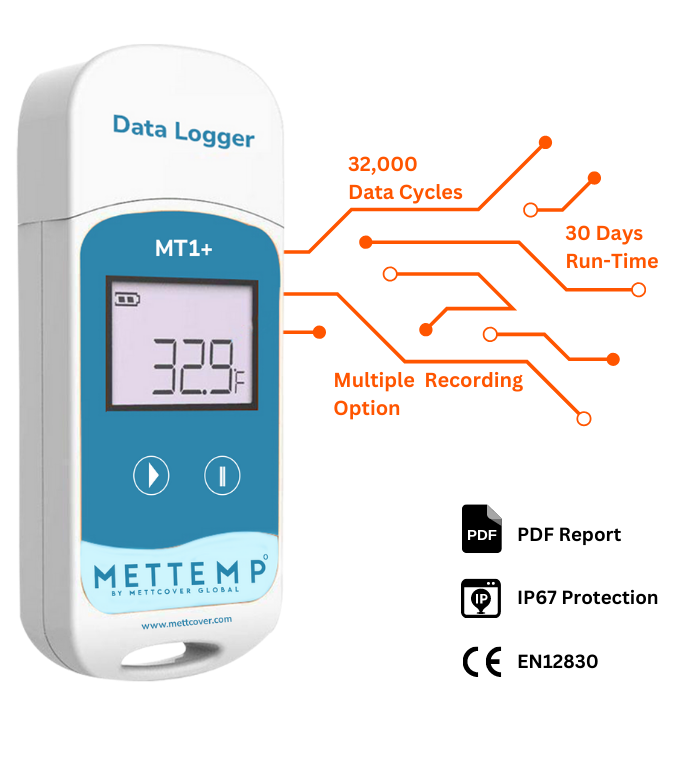
A good quality, multiple-use, temperature data-logger can give you multiple recording options and up to 32,000 data cycles. On an average it will facilitate 30 days run time on single-charge/battery yet, the actual run time may depend on the time intervals you may choose to record temperature events at. You can, however, calibrate the data logger to record temperature at time intervals that are best suited for effective monitoring as per the shipment’s temperature profile and ambient temperature variations anticipated during transit. While choosing data loggers, make sure that they are graded for IP67 Protection and are accredited with CE EN12830.
The data logger model shown in the corresponding image is MettTemp MT-1+ which is a multiuse data logger and features a readily downloadable and sharable PDF report of all data recordings. MT-1+ can record and monitor temperature range of (minus) -30 degrees Celsius to (plus)+70 degree Celsius with an accuracy of ±0.5℃ for (-20℃/+40℃). It has a default run time of 30 days with a reconfigure option for longer periods.
How do temperature data loggers work?
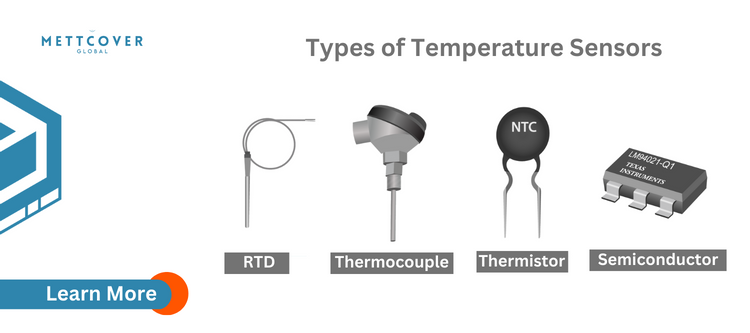
Temperature data loggers use a variety of temperature sensors to measure the temperature of a system. The most common types of sensors include thermocouples, resistance temperature detectors (RTDs), and thermistors. Each of these sensors has its own unique advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of sensor depends on the specific requirements of the application. Here’s how it works:
Thermocouples: Thermocouples are the most commonly used temperature sensors for data loggers. They consist of two metal wires, typically made of iron, nickel, or chromel, which are connected at one end to form a junction. When the junction is heated, a small voltage is generated which is proportional to the temperature of the junction. This voltage can then be measured by the data logger to determine the temperature of the system.
RTDs: Resistance temperature detectors (RTDs) are temperature sensors that use the resistance of a metal element to determine the temperature of a system. The resistance of the metal element changes with temperature, and this change can be used to determine the temperature of the system. RTDs are highly accurate and stable, but they also have a relatively slow response time, which can limit their use in some applications.
Thermistors: Thermistors are temperature sensors that use the change in resistance of a semiconductor material to determine the temperature of a system. Like RTDs, the resistance of the thermistor changes with temperature, and this change can be used to determine the temperature of the system. Thermistors are typically less accurate and stable than RTDs, but they have a faster response time and are often used in high-speed temperature monitoring applications.
Data Logger Storage and Transfer.
Temperature data loggers typically store the temperature data in non-volatile memory, such as flash memory or EEPROM. This allows the data to be stored even if the data logger is turned off or the battery runs out. Some data loggers also feature communication interfaces, such as USB or Ethernet ports, which allow the data to be easily transferred to computers and smartphones.
What are the developing trends in temperature data logger category?
The use of temperature data loggers in the cold chain industry is expected to continue to grow in the coming years, driven by increasing demand for high-quality, safe, and efficient supply chains.
Here are some of the key trends in this field:
Advanced Features: Temperature data loggers are becoming increasingly sophisticated, with advanced features such as real-time monitoring, wireless connectivity, and cloud-based data management. This is allowing companies to monitor the cold chain more effectively and make data-driven decisions to improve efficiency and reduce waste.
Integration with Other Systems: There is an increasing trend towards integrating temperature data loggers with other systems in the supply chain, such as transportation management systems and temperature control systems. This integration is helping to provide a complete picture of the cold chain and to improve overall efficiency and safety.
Increased Adoption in Emerging Markets: The use of temperature data loggers is expected to grow in emerging markets, such as Asia and Africa, as these regions continue to develop their cold chain infrastructure and regulations become more stringent.
Increased Focus on Sustainability: The cold chain industry is becoming increasingly focused on sustainability, with a growing emphasis on reducing waste and minimizing the environmental impact of the supply chain. Temperature data loggers can play a key role in this by helping companies monitor and reduce waste in the cold chain.
Development of New Technologies: There is ongoing development of new technologies in the temperature data logger field, including the use of AI and machine learning to analyze temperature data and make predictions about potential issues in the cold chain.
Temperature data loggers play a critical role in the cold chain industry, helping to ensure that perishable goods are stored and transported at the appropriate temperature to maintain their quality and safety. Despite some challenges, the use of temperature data loggers is expected to continue to grow in the coming years, driven by increasing demand for high-quality, safe, and efficient supply chains. Companies that invest in temperature data loggers and utilize them can certainly improve their supply chain efficiency and make data driven decisions for prolonged growth and profits.




