Enhancing Cold Chain Logistics: A Specifiers’ Guide to Supply Network Design
- Mettcover Global

It is most likely that you will learn it the hard way; in Cold Chain, there are no second chances.
-Anonymous
Cold Chain Logistic is a complex and dynamic relay-play where (for all the right reasons) the expertise and proficiency of cold chain specifiers shine brightly. These learned individuals embody the intellectual prowess of the industry as they meticulously plan, strategize, design and execute cold chain networks with the utmost precision and excellence. The fear of unknown cannot be nullified in cold chain channels as there are simply too many variables at play and Cold chain specifiers are the architects and visionaries who play a pivotal role in designing and implementing the most efficient and reliable cold chain systems.
This comprehensive cold chain management guide explores the key considerations that cold chain specifiers should keep in mind while creating reference models and architectures for cold chain routes.
Profile of the Precious Cargo
First and Foremost, to develop an effective SOP, specifiers must thoroughly understand the requirements of the shipments. While you cannot rule out the uncertainty, yet, the model must be designed (to withstand cold chain challenges) to the best of their capabilities. The intelligent probing in this case includes but are not limited to:
What is the Shipping Label Temperature Profile?
The first step in designing a cold chain system is determining the precise temperature range needed to maintain the product integrity throughout the entire transportation process. For instance, vaccines often require storage at temperatures between 2-8°C, while other perishable food items may have different temperature requirements. Selecting appropriate insulation materials and packaging solutions is crucial to maintain the desired temperature range and protect the products from temperature excursions.
How long will the shipment be in transit?
The expected duration of the shipment, including transit time, handling time, and potential delays, must be considered. Longer durations require more robust insulation and temperature control measures to ensure product stability. For example, pharmaceutical products with stringent temperature requirements may require specialized packaging solutions and active temperature monitoring systems for shipments that span multiple days.
Optimal Cold Chain Packaging. But How?
Evaluating the type of packaging used is essential to ensure product integrity. Containers, pallets, insulation materials, and other protective measures must be carefully chosen to provide adequate thermal insulation and protection against external temperature fluctuations. For instance, insulated containers and pallets equipped with phase change materials or vacuum insulation panels can help maintain stable temperatures during transportation.
Size Matters in Cold Chain.
Assessing the quantity and dimensions of the products being transported is crucial for optimizing the utilization of space and resources. It helps determine the appropriate capacity and logistics infrastructure needed to accommodate the shipment. By optimizing space utilization, cost efficiency can be achieved while ensuring the efficient flow of goods. For example, optimizing the arrangement of products within a container can minimize empty spaces and maximize the number of units transported.

Assessing the Complexity of the Cold Chain Network.
To design an efficient reference model, it is essential to assess the entire cold chain network. This involves:
Identifying stakeholders
The cold chain network comprises various stakeholders, including suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, transportation providers, and regulatory authorities. Collaboration and communication among these stakeholders are crucial to ensure the smooth flow of goods and adherence to quality standards. For example, close collaboration between pharmaceutical manufacturers and logistics providers is essential to maintain the integrity of temperature-sensitive drugs throughout the cold chain.
Analyzing Transportation Modes
Different transportation modes, such as air, land, sea, or multimodal options, have specific temperature control requirements and constraints. Specifiers must analyze the strengths and limitations of each mode and determine the most suitable options for the specific cold chain requirements. For instance, air transport may offer faster transit times but can be more susceptible to temperature fluctuations, requiring advanced temperature control measures.
Mapping the Supply Chain
Understanding the complete supply chain is crucial for identifying critical control points and potential vulnerabilities. Specifiers should map the last mile, middle mile, first mile, and key points where temperature integrity must be maintained. Implementing appropriate monitoring and control measures at each stage ensures the preservation of product quality. For example, in the pharmaceutical industry, mapping the supply chain helps identify potential risks during distribution, such as exposure to extreme temperatures during customs clearance.
Compliance Requirements:
Compliance with relevant regulations and certifications is vital to ensure product safety and regulatory compliance. Specifiers must familiarize themselves with standards such as Good Distribution Practices (GDP) and Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP). Adherence to these standards is critical for quality assurance and regulatory compliance. For example, compliance with GDP ensures proper storage, transportation, and distribution of pharmaceutical products, minimizing the risk of temperature excursions and maintaining products’ efficacy.
Cold Chain Network Assessment
| Elements | Details |
| Identifying Stakeholders | Suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, transportation providers, regulatory authorities |
| Analyzing Transportation Modes | Air, land, sea, multimodal |
| Mapping the Supply Chain | Last mile, middle mile, first mile, critical control points |
| Compliance Requirements | Good Distribution Practices (GDP), Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) |
Cold Chain Technologies? Order what you can consume.
Utilizing suitable technologies is crucial for effective cold chain management. However an oversight can easily increase your Total Cost of Ownership (TCO). Use technologies that give a robust ROI on the fright and shipment value. Consider your needs and budget before integrating the technology, however, do not ignore them.

Temperature Monitoring Systems
Implementing robust temperature monitoring devices and systems is essential to track and record temperature data throughout the shipment journey. Advanced sensors and data loggers can provide real-time information and alerts in case of temperature excursions. For instance, wireless temperature sensors and data loggers with cloud-based data storage and analytics platforms enable continuous monitoring of temperature-sensitive products.
Data Logging and Analysis
Advanced data logging and analysis tools help gain insights into temperature variations, potential risks, and deviations from set parameters. Statistical analysis of temperature data can identify patterns and optimize cold chain processes. For example, cloud-based analytics platforms can analyze temperature data to detect trends and predict potential temperature excursions.
Real-time Asset Tracking
Incorporating real-time tracking technologies enhances visibility and traceability of shipments, enabling proactive interventions if issues arise. GPS tracking and monitoring systems provide real-time location information and enable monitoring of temperature conditions during transit. This helps in identifying any deviations or delays and allows for prompt corrective actions.
Integration and interoperability
Ensuring seamless integration and interoperability of technologies across the entire cold chain network is crucial for efficient data exchange and communication. Standardization of data formats and communication protocols enhances data accuracy and enables efficient decision-making. For example, using standardized data formats and protocols allows for seamless data exchange between different stakeholders in the cold chain.
Technology Reloaded.
| Technologies | Details |
| Temperature Monitoring | Wireless temperature sensors and data loggers |
| Data Logging and Analysis | Cloud-based analytics platforms |
| Real-time Tracking | GPS tracking devices and monitoring systems |
| Integration and Interoperability | Standardized data formats and communication protocols |

Risk Analysis and Management
Identifying and mitigating risks is vital in cold chain logistics. Specifiers must consider the following strategies:
Contingency Planning
Developing robust contingency plans to address potential risks is essential. These plans should include backup power systems, emergency response plans, and alternative transportation arrangements. By being prepared for equipment failure, power outages, natural disasters, or delays in transit, specifiers can ensure a prompt response to unexpected events.
Risk assessment
Conducting a comprehensive risk assessment helps identify vulnerabilities and develop appropriate risk mitigation strategies. This includes analyzing the impact of temperature excursions, potential hazards during handling and storage, and security risks. For example, hazard analysis can identify potential risks associated with specific products, such as the sensitivity of certain medications to temperature fluctuations.
Training and Standard Operating Procedures
Implementing rigorous training programs for personnel involved in cold chain operations is crucial. Well-trained staff plays a critical role in maintaining temperature integrity and handling emergencies effectively. Establishing standardized operating procedures (SOPs) ensures consistency and compliance throughout the cold chain. For instance, training programs can educate personnel on proper handling procedures and the use of temperature monitoring devices.
Risk Mitigation Strategies and Scope in Cold Chain Management
| Strategy | Scope |
| Contingency Planning | Backup power systems, emergency response plans |
| Risk Assessment | Hazard analysis, temperature excursion impact assessment |
| Training and SOPs | Training programs for cold chain personnel, SOPs for handling and storage |
Creating effective reference models and architectures for cold chain shipments requires a thorough understanding of shipment requirements, comprehensive assessment of the cold chain network, selection of appropriate technologies, and robust risk mitigation strategies. By considering these key factors, cold chain specifiers can contribute to the development of efficient and reliable cold chain systems that ensure the integrity and quality of temperature-sensitive products throughout their journey.
Passive insulation solutions play a vital role in the design and implementation of a foolproof model and architecture for cold chain shipments. These solutions, such as Thermal Pallet Covers, Air Cargo Covers, and Container Liners, offer significant benefits in maintaining temperature integrity and ensuring the quality of temperature-sensitive products. Let’s explore how these passive insulation solutions help specifiers in creating a robust cold chain system.

Thermal Pallet Covers in 16+ advanced Insulation Material Grades.
Thermal Pallet Covers are designed to provide effective thermal insulation and protection for palletized goods during transportation. These covers are made of high-quality materials with excellent insulation properties, such as reflective foils and insulating layers. By simply placing a Thermal Pallet Cover over the pallets, specifiers can create a thermal barrier that minimizes temperature fluctuations and helps maintain the desired temperature range.
Imagine a scenario where pharmaceutical products need to be transported within a specific temperature range of 2-8°C. Specifiers can incorporate Thermal Pallet Covers to ensure that the temperature-sensitive drugs remain within the required temperature range throughout the shipment. The covers act as a protective shield against external temperature variations, preventing heat transfer and minimizing the risk of temperature excursions.
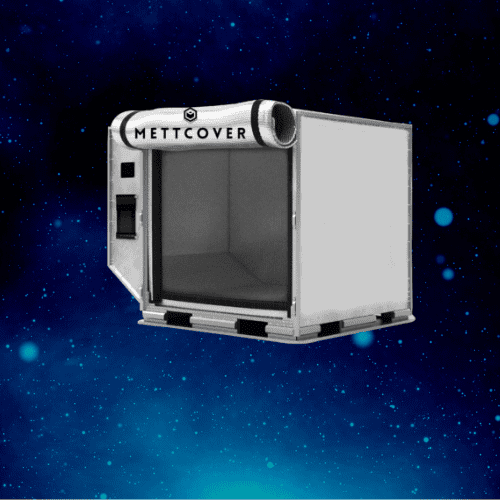
Air Cargo Thermal Covers & Insulated Liners.
Air Cargo Covers are specially designed insulated covers that provide thermal protection for airfreight shipments. These covers are lightweight, easy to install, and offer excellent insulation capabilities. They create a barrier between the cargo and the external environment, reducing heat transfer and maintaining a stable temperature during air transportation.
For instance, consider the transportation of fresh fruits from a tropical region to a distant market. Specifiers can utilize Air Cargo Covers validated to shield the perishable fruits from temperature extremes during airfreight and maintain pallet load temperature in desired range. By incorporating Mettcover Thermal Covers, the cold chain architect can ensure that the fruits arrive at their destination in optimal condition, without compromising their quality and freshness.
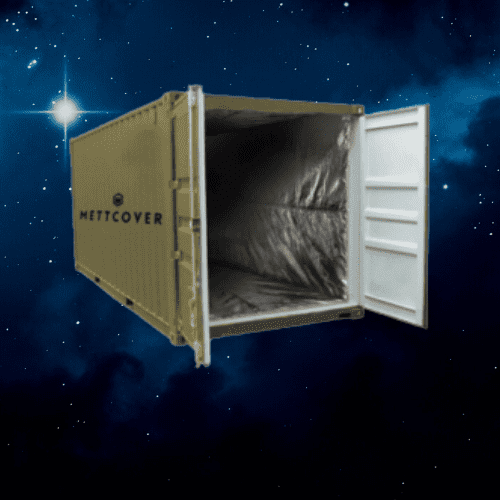

DIY Container Liner Kits maintain temperature integrity and combat container rain.
Container Liners are insulation materials that are placed inside shipping containers to provide thermal protection for bulk shipments. These liners are designed to minimize heat transfer, control temperature fluctuations, and provide an additional layer of insulation for the cargo.
Let’s imagine a scenario where a large quantity of dairy products, such as milk and cheese, needs to be transported in a shipping container. Specifiers can incorporate Container Liners to create a thermally controlled environment within the container. These liners help maintain the required temperature range, prevent condensation, and ensure that the dairy products remain fresh and safe throughout the journey.
By utilizing passive insulation solutions like Thermal Pallet Covers, Air Cargo Covers, and Container Liners, specifiers can enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of cold chain shipments. These solutions contribute to the creation of a foolproof model and architecture. Passive insulation solutions act as barriers, reducing heat transfer and minimizing temperature fluctuations that can compromise the quality of temperature-sensitive products. The use of thermal covers and liners adds an extra layer of insulation and protection, shielding the cargo from external temperature variations and potential hazards. By maintaining the desired temperature range, passive insulation solutions ensure that products remain within their required specifications throughout the entire transportation process. The inclusion of passive insulation solutions helps mitigate the risk of temperature excursions and potential product damage, thus improving the overall reliability of the cold chain system.




