How to Place Data Loggers in an Airfreight Container and a 20 feet Shipping Container?
- Seetarama Rao
- November 3, 2023

Minimizing consignment rejection with precision temperature & humidity recording, and correct placement of data loggers during the intermodal transit of pharmaceutical shipments.
In the pharmaceutical cold chain management, the stakes are high. Data logger reports are the litmus test for pharmaceutical shipments. When these reports reveal temperature excursions beyond the bounds of permissible limits, the implications are dire: consignment rejection, financial losses, and most crucially, patient safety at risk. Therefore, in the unforgiving ecosystem of pharmaceutical supply chain management, precision is the only reason for success.
This white paper is a comprehensive guide that dissects the rationale of placing data loggers during the intermodal transit of pharmaceutical shipments. The journey of temperature sensitive medicines begins in a warehouse, where they are carefully loaded in pallets. From this point, we traverse the often complex path of transitioning these critical cargo units onto truck transport and ultimately into the secure confines of air cargo units for their final transit. Amidst this meticulous process, the pallets are protected with thermal pallet covers. An effective radiant and heat barrier, shielding the pallet load from the capricious extremes of temperature on tarmac and beyond. A very important element of stacking the boxes inside of a pallet is the placement of data loggers. It is imperative that data logger reports align with the shipment’s temperature profile and that the temperature of the pallet load does not breach its prescribed integrity.
The white paper explores not just the “how,” but the “why” behind this critical placement. With standard US pallet sizes, covered with Mettcover BUB 901 thermal pallet covers as subjects, we explore the precise locations where the temperature data loggers must be placed throughout the intermodal transit of life saving medications.
Introduction
In temperature controlled logistics, every step of the journey is a careful plan. In this introductory section, we set the stage for our exploration of a critical element within the cold chain: the placement of data loggers. The pharmaceutical cold chain is the backbone of the healthcare industry. It encompasses a series of temperature-controlled steps, from manufacturing to storage and distribution, ensuring that medications retain their potency and safety. These products, ranging from vaccines to biologics, are often biologically active compounds, making temperature control paramount throughout their life cycle.
The regulatory authorities, such as the World Health Organization (WHO) and the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), have set stringent standards for temperature-sensitive pharmaceuticals. These standards ensure that products remain within specific temperature ranges during transit to maintain their efficacy and patient safety. However, maintaining this delicate balance is not without its challenges. Temperature fluctuations can occur at any point during transit, jeopardizing the integrity of pharmaceuticals. It’s at this juncture that data loggers emerge as a resolute entity to continuously monitor and record temperature data to safeguard product quality. This white paper’s core focus is on the precise placement of data loggers. To make the most of these devices, it is essential to strategically position them within pallets and thereafter correctly place the pallets in the transport mediums. In this paper, we will discuss the placement of pallets and data loggers in an air freight container and a 20 ft container truck.
Research Questions
Q 1 – Does the placement of data loggers matter in cold chain management?
Q 2 – What should be the correct placement of data loggers in an air freight container and a 20ft container?
Research Methodology
In scientific context, theory must become practice. At Mettcover Global, we strive to have an active dialogue with our customers to implement best practices that are mutually beneficial and profitable. In this paper, we are using a ‘Comparative Case Study’ method as our conclusion is derived from two case studies. The first being a leading pharmaceutical manufacturer who constantly faced the challenge of transporting biologics across long distances. By strategically placing data loggers within Unit Load Devices (ULD), they achieved a remarkable reduction in temperature excursions. The precise placement of loggers allowed them to identify and rectify specific areas within the ULD pallets that were prone to temperature fluctuations. The data insights empowered the company’s Quality Team to consistently maintain the product quality and efficacy, earning the trust of their customers and regulatory agencies.
Another case study highlights the significance of logger placement in transport trucks. A pharmaceutical distributor in Indonesia, specializing in rare disease medications regularly transports temperature-sensitive products in remote regions. By adhering to best practices in logger placement, they were able to correctly map out the temperature profiles within the truck and rectify the loopholes of their process. This not only safeguarded product quality but also expanded their market reach, providing critical medications to underserved communities.
The primary data from the comparison analysis enables us to form a logical observation about the placements of data loggers that work best in mapping temperature excursions and variations during transit tenure of a pharmaceutical shipment via road and air transport mediums.
In addition to this, we are also adopting an interpretive research philosophy, emphasizing the subjective understanding of social phenomena (Collis & Hussey, 2014). Interpretivism underscores the construction of knowledge through collaboration and individual experiences also known as the secondary research resources. Through a thematic analysis of existing literature, this research philosophy allows for a deeper exploration and understanding of available data. It provides an opportunity to synthesize and critically evaluate existing research to derive meaningful insights and draw relevant conclusions. This approach aligns well with our research objectives, facilitating a comprehensive examination of what is the correct placement of data loggers in an air freight container and a 20 feet container truck.
Data Logger Placement in Cold Chain Management: Does It Matter?
Several research studies and industry reports have investigated the impact of data logger placement on the efficacy of cold chain management. Qu and Soh (2015) explored the optimal placement of temperature loggers in air cargo containers for pharmaceutical shipments. Their findings underscored the importance of strategic positioning to ensure accurate temperature monitoring. By placing loggers at specific locations within cargo containers, such as the top, center, and bottom positions, temperature variations could be effectively captured.
Ahmed et al. (2014) conducted a comprehensive review of temperature profiling and cold chain management in the pharmaceutical industry. While their focus was not primarily on logger placement, their work highlighted the critical role of temperature monitoring in ensuring pharmaceutical product quality and safety. This indirectly emphasizes the significance of well-placed temperature loggers within cargo containers.
Determining The Correct Placement of Data Loggers in Air freight Containers and 20ft Containers.
Data logger placement varies depending on the type of container used for pharmaceutical shipments. In air freight containers, precise placement is essential due to the unique challenges of air transport. Researchers like Qu and Soh (2015) recommend a multi-tiered approach, where Logger 1 is placed at the top, Logger 2 at the center, and Logger 3 at the bottom. This strategy leverages temperature stratification, capturing variations at different vertical levels within the container. For 20ft container trucks, Huh, Koo, and Yang (2016) have focused on temperature mapping and monitoring within refrigerated vehicles, shedding light on logger placement within mobile environments. While they primarily concentrate on vehicles, their insights extend to the importance of well-placed loggers. The front position (Logger 1), rear position (Logger 2), and center position (Logger 3) are recommended to address temperature variations effectively.
Data Logger Placement in Air freight Containers
Air freight containers are vital in the swift and efficient transportation of pharmaceuticals across vast distances. To ensure the temperature-sensitive cargo’s integrity, precise data logger placement is imperative.
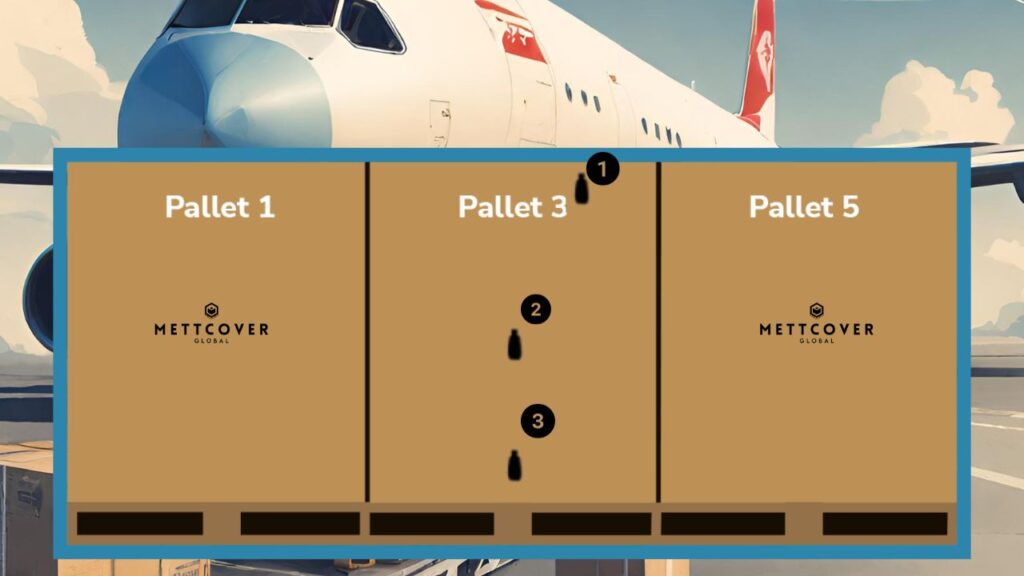
- Logger 1 (Top Position): Logger 1 should be strategically placed at the top of the airfreight container. This location ensures that it is exposed to the warmest air rising within the container. Placing Logger 1 at the highest point allows for the monitoring of temperature extremes that may affect the uppermost layer of cargo.
- Logger 2 (Center Position): Logger 2 is ideally situated in the center of the cargo load. Placing it at this position allows for monitoring temperature conditions that are representative of the majority of the pharmaceutical cargo within the container. It acts as a beacon, capturing the temperature profile of the core cargo, providing insights into the overall thermal stability of the shipment.
- Logger 3 (Bottom Position): Logger 3 should be placed at the bottom of the airfreight container. This position allows monitoring of the coldest air that settles at the container’s base. Placing Logger 3 here is vital for capturing any temperature fluctuations that may occur in the lower portion of the cargo stack. It helps in assessing the effectiveness of temperature control at the container’s base.
The rationale behind this placement strategy is rooted in the principles of temperature stratification. Air inside a container tends to stratify, with warmer air rising to the top and cooler air settling at the bottom. By positioning loggers at different vertical levels within the container, we gain a comprehensive understanding of the temperature distribution. Logger 1, at the top, serves as an early warning system for potential temperature excursions originating from external factors or heat generated within the container. Logger 2, in the center, represents the core cargo temperature and provides insights into the overall stability of the shipment. Logger 3, at the bottom, ensures that even the coldest regions are monitored, addressing any potential issues related to cold spots or poor airflow.
Data Logger Placement in 20ft Container Trucks
20ft container trucks play a vital role in pharmaceutical logistics. Proper data logger placement within these trucks is equally critical to maintain temperature control.
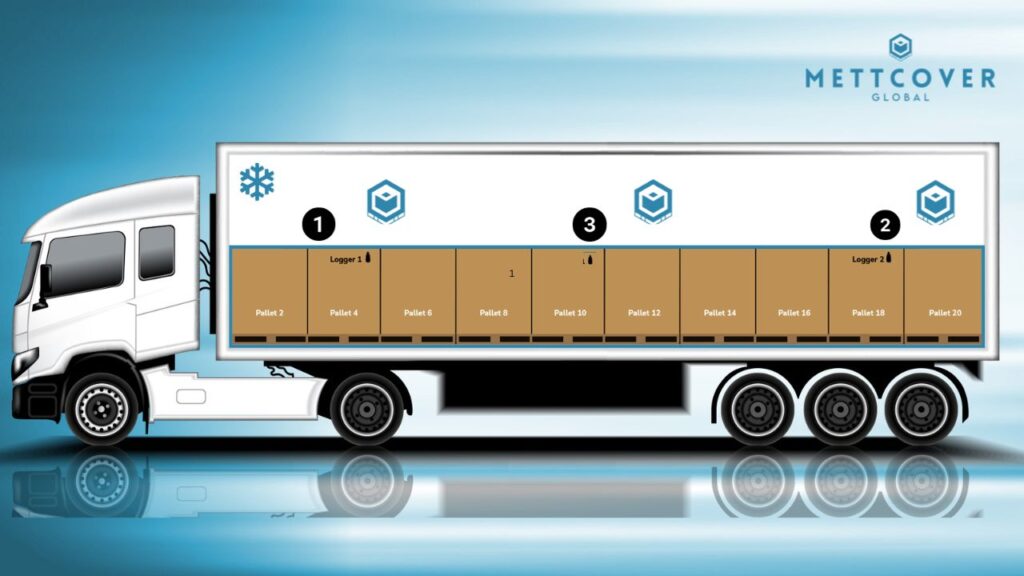

- Logger 1 (Front Position): Logger 1 should be placed at the front of the 20ft container truck, about 1.2–1.4 meters from the cargo’s bottom. This location allows for monitoring of temperature conditions at the front of the cargo load, where temperature variations may occur due to external factors or poor airflow.
- Logger 2 (Rear Position): Logger 2 is ideally situated at the rear of the cargo load, mirroring the placement of Logger 1. Placing Logger 2 at this position ensures balanced temperature monitoring throughout the cargo stack.
- 1Logger 3 (Center Position): Logger 3 should be placed at the center of the cargo load, aligned vertically with Loggers 1 and 2. This strategic placement ensures comprehensive temperature monitoring, with Logger 3 capturing conditions representative of the core cargo stack.
The placement of Loggers 1 and 2 at the front and rear of the cargo load is designed to address potential temperature variations that may occur due to external factors, such as heat entering the truck from the environment or varying airflow conditions. Placing Loggers 1 and 2 symmetrically helps ensure that temperature differences are identified and mitigated effectively. Logger 3’s placement at the center aligns with the core cargo stack, providing valuable insights into the temperature stability of the majority of the pharmaceutical shipment. This strategic placement ensures that temperature data from the cargo’s heart are accurately monitored, allowing for timely intervention if deviations occur.
In both air freight containers and 20ft container trucks, the precise placement of data loggers at different vertical levels within the cargo load allows for a thorough assessment of temperature conditions. This multi-tiered monitoring strategy enhances the pharmaceutical supply chain’s robustness, ensuring that temperature-sensitive medications arrive at their destination in optimal condition, compliant with regulatory standards, and safeguarded against consignment rejection.
Conclusion
Correct placement of data loggers, as discussed in previous sections, is not merely about adhering to regulatory standards—it goes beyond compliance. It’s about creating a true-data map of temperature conditions within pallets and containers to safeguard the integrity of critical pharmaceutical medicines.
In pharmaceutical cold logistics, the mean readings provided by strategically placed data loggers offer more than just compliance assurance. They offer a comprehensive view of temperature variations across the entire shipment. Here’s why this matters:
- Ensuring Compliance with Precision: The mean readings derived from the three strategically placed loggers provide a precise and comprehensive picture of temperature deviations within the pallet or container. This level of accuracy ensures that pharmaceutical companies meet compliance standards consistently and confidently.
- Safeguarding Medication Integrity: Beyond compliance, these mean readings are instrumental in safeguarding the integrity of temperature-sensitive medications. Temperature excursions, even within permissible limits, can still affect the potency and safety of pharmaceuticals. The mean readings capture these subtle variations, allowing for proactive interventions to maintain medication efficacy.
- Fulfilling the Purpose of Healthcare Goodness: Pharmaceutical logistics isn’t just about moving products; it’s about ensuring that these products fulfill their ultimate purpose—improving patient health. The meticulous mapping of temperature conditions, made possible by the correct placement of data loggers, aligns with the overarching goal of healthcare goodness. Patients can have confidence that the medicines they receive are not only compliant but also uncompromised in quality.
- Elevating Patient Trust: When pharmaceutical companies go the extra mile to ensure temperature control beyond compliance, it elevates patient trust. Patients and healthcare providers appreciate the commitment to quality and safety. This trust is invaluable in an industry where patient well-being is paramount.
In conclusion, mapping temperature conditions through precise logger placement is a multifaceted endeavor. It ensures regulatory compliance, safeguards medication integrity, fulfills the purpose of healthcare goodness, and elevates patient trust. Correct logger placement is not just a regulatory requirement; it’s a testament to a pharmaceutical company’s commitment to delivering uncompromised healthcare solutions to those who need them most.
The Crucial Role of Data Loggers in the Cold Chain
Data loggers are indispensable instruments in the pharmaceutical cold chain, ensuring the safe and effective delivery of temperature-sensitive medications. In this section, we delve into the multifaceted significance of data loggers, covering various aspects of their pivotal role.
- Ensuring Regulatory Compliance: Compliance with stringent regulatory standards set forth by organizations like the FDA (Food and Drug Administration) and WHO (World Health Organization) is paramount in pharmaceutical logistics. These regulations mandate the maintenance of specific temperature conditions during storage and transportation. Data loggers serve as the sentinels of compliance, continuously monitoring temperature conditions and recording critical data points. This ensures that pharmaceutical companies meet regulatory requirements with precision and accuracy. Proper logger placement is essential to capture temperature variations effectively throughout the supply chain, aligning with regulatory expectations.
- Mitigating the Risk of Consignment Rejection: Consignment rejection due to temperature excursions is a costly and reputation-damaging consequence in pharmaceutical logistics. Precise data logger placement plays a pivotal role in mitigating this risk. By strategically positioning loggers within cargo containers, temperature variations are captured with precision, allowing for swift corrective actions in the event of deviations. This proactive approach safeguards pharmaceutical shipments from rejection, minimizing financial losses and preserving brand reputation.
- Enhancing Product Quality and Safety: The impact of data loggers in pharmaceutical logistics goes beyond regulatory compliance; it directly influences product quality and patient safety. Temperature-sensitive medications are highly susceptible to temperature fluctuations that can compromise their efficacy and safety. Proper logger placement ensures that these products remain within the specified temperature range, preserving their quality throughout the supply chain. Patients can trust that the medications they receive have been transported under optimal conditions, free from temperature-induced degradation.
- Ensuring Precision in Pharmaceutical Logistics: Pharmaceutical companies can leverage precise data logger placement as a competitive advantage. By investing in state-of-the-art data loggers and implementing strategic placement strategies, they can ensure precision and reliability in their logistics operations. This not only demonstrates commitment to product integrity but also sets them apart in a highly competitive industry.
- Elevating Brand Reputation: Through data transparency and a commitment to temperature control, companies can enhance their brand reputation. When patients and healthcare providers have confidence in a brand’s commitment to product safety and efficacy, it elevates the brand’s standing in the market. An impeccable track record in pharmaceutical logistics builds trust and fosters loyalty.
- Building Trust Through Data Transparency: Pharmaceutical companies can build trust with various stakeholders, including customers and regulatory agencies, by providing transparent temperature data throughout the supply chain. By sharing data logger records and temperature reports, they demonstrate a commitment to transparency and accountability. This not only meets regulatory expectations but also fosters strong relationships based on trust and reliability.
Not sure if you are using the data logger correctly or even a correct data logger? If you have any questions about temperature data loggers or wish to learn more about Mettemp Data Loggers, please feel free to connect with me.




